Hi Readers. The other day I asked for some feedback on what you want to learn more about. I got a reply asking to explore more about AI or Artificial Intelligence.
When you hear AI, what is the first thing that comes to mind? Are you an enthusiast, knowing the first AI were used to play chess against humans? Do you think of Alexa, the AI on Amazon devices, or being able to say “Hey Google!” to your android phone(Siri for iPhones)? Do you recall AI like Sohpia the human-like robot who can tweet, hold a conversation and so much more! Maybe your mind goes to the technical side, to ML (Machine learning). All of these are under the umbrella of artificial intelligence. This post will be talking about several AI projects from the last 10 years to today.
Before we get into specific and exciting tech let’s lay some groundwork. In order for any AI to operate they have to be taught first.
Imagine you are trying to teach a child how to get ready for bed. First you would do the things for them to give them the general structure: brushing their teeth, washing their face, etc… Then once they know the steps, you would monitor them to verify they can do it themselves, correcting any mistakes they make in the process. Machine learning (ML) is a lot like this example. We teach computers how to do a task and then monitor them until they have an acceptable success:fail ratio for deployment. ML allows computers to explore data and recognize patterns. An example would be YouTube suggesting relevant videos to you. It makes a prediction based on your watch history, your location and its internal data on videos you haven’t watched yet. ML is essentially the term for teaching AI or machines.
Deep learning(DL) is a subset of ML. Deep learning is ML that is based off of the human brain. AI that learn with deep learning will have an artificial neural network. DL requires a large data set to teach the machine. This is both expensive and time-consuming as you often need GPU’s which possess higher processing power. AIs that employ DL will take in a data-set, teach themselves to recognize patterns and then give predictions based on what it learned. Neural networks are how we model the human brain. These networks are made up of artificial neurons. They have an input and output layer, and some layers in between that help AI decipher information it takes in.
Before Deep learning existed AI was dominated by Symbolic AI AKA Good, Old-Fashioned AI. Symbolic AI does not require massive amounts of data like other ML. It does not ensue training or guesswork like other methods either. Symbolic AI do have access to a knowledge base- symbols to represent our real world. By representing problems as symbol it uses logic to problem-solve. Symbolic AI use relational statements. Let’s say we have a strawberry donut. We can represent symbols inside ().
So:
(donut)
Relations are used as descriptors, descriptors are shown next to the symbol, so:
strawberry(donut)
Let’s say I eat this donut:
Eat(Nia, Donut)
Symbolic AI uses truth tables, or propositional logic to understand the world around it.
Let’s say I am eating a freshly baked strawberry donut.
| fresh(donut) | strawberry(donut) | Eat(Nia,donut) | fresh(donut) AND strawberry(donut) AND Eat(Nia,donut) |
|---|---|---|---|
| true | true | true | true |
If you’ve ever taken a discrete math class, this is an AND truth table. You’d know that for the last column to be true the first 3 must also be true. AND meaning propositional logic or gates. AND is true when both statements are true and false if one or more statement is false. Another common gate is OR, which is true if either statement is true, and false if both are false.
This is a short example of how an AI could come to understand a situation. It would most likely see true as 1, and false as 0. It would compute AND as multiplication and OR as addition. Symbolic AI has these and other gates at its disposal to figure out the world and solve problems. It is admirable how they accomplished so much with so little, before the advent of Deep Learning.
Natural language processing(NLP) allows AI to understand our everyday language. It grants them the ability to translate sentences from one language to another. This is because it can understand the meaning of a sentence. NLP is rule based human language. It is often used with Deep learning(Neural NLP) to help enhance AI’s ability to understand voice commands. NLP includes speech recognition, sentiment analysis, understanding references, and name entity recognition. (Ex: understanding that Seattle is a city, or that Yessenia is a person’s name). NLP also deals with natural language generation; coming up with sentences on its own to respond to users. This type of ML is used in a lot of AI because the everyday user will still need to communicate with its machine and direct it to use it. Previous to Deep learning, NLP was used with Symbolic AI or Symbolic NLP.
10 years ago when you heard of AI the connotations were either gaming (both video games and popular game shows) or the budding virtual assistants.
In 2010 Microsoft came out with the “Kinect” for it’s Xbox 360 console. It was the first gaming device to track human movements using infrared and a 3D camera. It uses AI algorithms to process the data it receives about your environment through its lens. Then in turn it controls the console without a physical controller. Kinect was taught through machine learning how the human body works, so it correctly digests the input it receives. It was taught to understand depth: how close or far you were to it in view of you, as well as detecting the different parts of a person. Telling apart our arms from legs, head from chest, etc. The same technology is used in a kinect sign language translator. You can explore Kinect’s other uses here.
IBM released its question-answering computer “Watson” in 2010. It could answer questions if posed in natural language. Watson is used for information retrieval, advanced natural language processing, knowledge representation, and automated reasoning. All of these skills applied to questions and answering, open to nearly any topic. Watson competed against Ken Jennings and Brad Rutter some of Jeopardy!’s top past players. Watson won against both of them in practice runs before airing, and twice in two actual games. Watson also played against US Congress members, also claiming a win. You can read more in detail here.
In 2007 SRI Artificial intelligence center developed the template for what would later become Siri. Apple acquired the tech in 2010, tweaking it for their IOS devices before releasing it in 2011. Siri is the first modern digital virtual assistant. Siri uses NLP and machine learning to aid its users.
Alexa, Amazon’s virtual assistant was debuted in 2013. Alexa like other assistants can process natural language questions, and as of 2018 can even have back and forth dialogue with its users. Alexa was taught with Deep learning. In 2019 The Verge reported 100 million devices with Alexa on them had been sold.
Following Apple’s lead Microsoft developed their virtual assistant Cortana. It was released for their phones in 2014, expanding it onto PC’s in 2015. Microsoft eventually discontinued the assistant on their phones in 2017. Again, like the other virtual assistants, NLP plays a big part as well as DL.
AI from 5 years ago to today have branched out into so many different areas unlike 10 years ago. We are on the brink many amazing discoveries in multiple areas. Some areas include entertainment, business, and general research.
Google also followed suit of Apple and Microsoft and released their Google Assistant in 2016. Today it comes standard on phones, Google home and home-mini and more. The same NLP is used as well as DL to interact and understand its user’s better as well as provide more accurate searches and help with tasks.
Hanson Robotics had us on the edge of our seats in 2016 when they debuted Sophia, a human-like robot. “She” was created for researching human-robot interactions, and it’s potential applications for entertainment. Sophia is the first robot Innovation Ambassador for the United Nations Development Programme. Like IBM’s Watson, Sophia uses NLP, in addition to neural networks, symbolic AI and more. Sophia uses machine perception and can recognize human faces and even has emotions. Explore more about Sophia here.
Facebook Artificial Intelligence Research(FAIR) lab created two chat-bots in 2017. Both bots used machine learning algorithms to teach them how to converse. FAIR had both chat-bots learn how to negotiate. They were given a set of items (each having a point value) and told to split the items between themselves and someone (human) or something (another chatbot or other AI) else. Eventually to develop more of this skill they had these chat-bots go through “Reinforcement Learning” with each other. Left to their own devices the two chat-bots deviated from their normal negotiation patterns. They eventually created a new way of communicating that diverged from human language. We know that they were communicating because points were still awarded when a trade was made. Even if the language looks like gibberish to the human eye, it is still indicative of the bots trying to negotiate. The situation was unexpected, but it helped further AI research. Specifically, how AI operate when not being pushed to do what we want them to do, what do they choose to do? For it’s desired purpose the project was a failure and eventually shut down. From an objective point of view research can be drawn, taken and used from this instance. You can read more here. You can find the github repo and view the code or deploy it yourself!
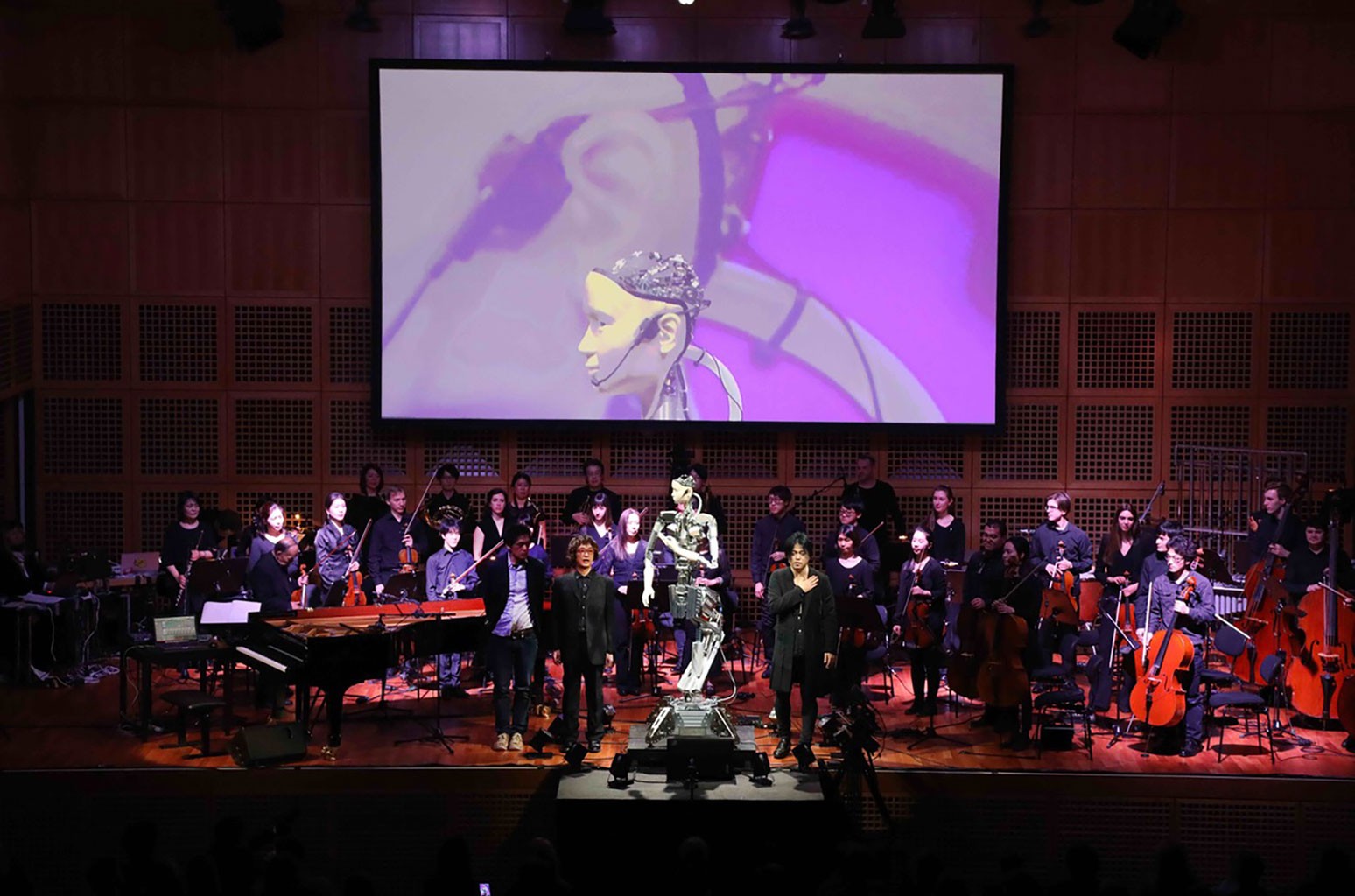

The next piece of AI is a jointly developed project from researches at the University of Tokyo and Osaka University. They released Android Alter 3 in 2018. Its purpose is the similar to Sophia, to understand how humans would react to an autonomous robot. The researchers hope to “explore fundamental questions of whether robots can obtain a sense of life, and what life itself may mean.” Android Alter has prosthetic skin for it’s face, neck and arms, it was not designed to be identical for humans. This AI actually conducts a human orchestra. Its movements are based on a CPG (central pattern generator) which functions like a human spinal cord. Alter 3 also uses a neural network. This project has had performances around the world, from Australia to Japan and even Germany. The piece Alter 3 conducts is called “Scary Beauty” produced by Keiichiro Shibuya. Alter 3 decides the tempo, volume and singing expression. Here is a clip of a performance in Tokyo.


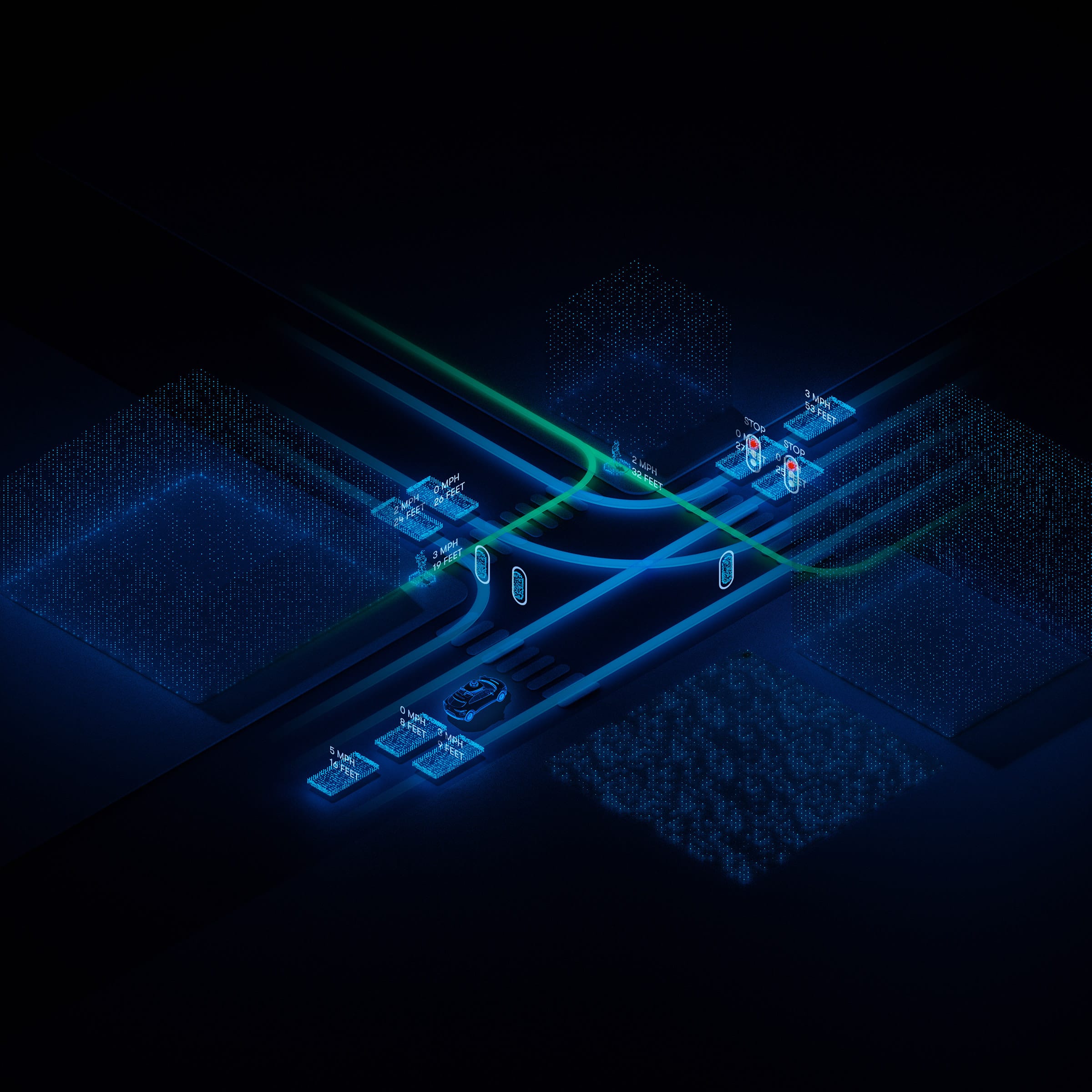

If you recall in 2008 Google was starting development on self-driving cars, or autonomous vehicles. In 2009 Google founded Waymo with the specific purpose to keep working on self-driving cars. 9 years later Waymo Driver had its debut. The technology can be applied to several car models and in Phoenix Arizona you can catch a ride on the Waymo One. It is like Lyft or Uber, you can use their app to get a ride around the city, except Waymo One drives itself. This tech has been tested in 10+ states and Waymo asserts they are “The most experienced driver in the world”. Waymo Driver has driven billions of miles in simulation and millions of miles on public roads. In addition to Waymo One for people Waymo Driver can also be used on trucks or what they call Waymo Via for moving goods across the country. Waymo Driver uses machine learning to detect the things around it as it drives. Whether it’s other cars, cyclists or pedestrians, it predicts what they may do and takes precaution accordingly. You can explore more about Waymo here.
In February 2020 Baidu a Chinese tech company aided in the development of covid-19 vaccines with their LinearFold AI algorithm. According to Baidu:
"LinearFold predicts the secondary structure of the ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequence of a virus—and does so significantly faster than traditional RNA folding algorithms. LinearFold was able to predict the secondary structure of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA sequence in only 27 seconds, 120 times faster than other methods. This is significant, because the key breakthrough of covid-19 vaccines has been the development of messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines. Instead of conventional approaches, which insert a small portion of a virus to trigger a human immune response, mRNA teaches cells how to make a protein that can prompt an immune response, which greatly shortens the time span involved in development and approval."
It is not specified what AI learning techniques were used, or how the algorithm was developed. I thought the inclusion of AI in the medical field was too significant to not mention.

In June of this year my partner took me on a date to the Immersive Van Gogh exhibit here in NYC. While it was enchanting and exciting, I mention it because at the end in the gift shop you could scan a QR code and receive a “letter from Van Gogh”. You guessed it! They had an AI read all Van Gogh’s past letters and trained it to write in his style. You give the AI your name as ask it a question, or give it some sort of topic and “he” will write you your very own letter. Receive your own letter here.
I have highlighted interesting and important AI here, but here is a more comprehensive list if you wish to learn more. Also of note is a organization that hopes to teach the AI leaders of tomorrow, AI for kids.
While writing this I’ve found myself a little inspired. If you can think of a fictional AI from a game, movie, TV show or anime comment it! I plan to compare fictional AI to real-world AI, and see what tech we have surpassed, measure up to, and hope to achieve in the future.
Thank you for reading!
